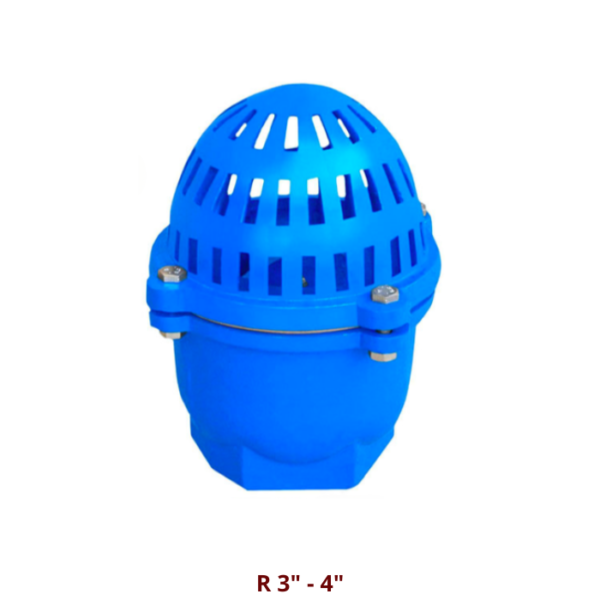
Our suction valve or foot valve prevents pump depriming if installed in a vertical position. It allows the passage of water in only one direction, to work without fluid in the other and avoid unwanted emptying. The force of the fluid causes the valve to open by forcing the disc and when the flow of fluid stops, it closes automatically.
It is designed to ensure that the pump supply line always remains full of water. It has a simple design without springs, using a disc in the small steps or a pair of clappers in the larger steps and they have a rubber sealing gasket. The installation of the foot valve must be carried out vertically (hence the name foot valve) to ensure its correct operation.
The foot valve has a strip that acts as a hinge with the sealing disc. When the pump begins to operate, the suction force exceeds the weight of the disc and the water column, which causes the foot valve to open, allowing water to be pumped without any interference and when the pump is turned off, the Disc weight and water column combine to automatically and airtight close the foot valve. This feature ensures that the pump supply line is always kept full of water, facilitating quick and safe start-up with every operation.
The foot valve acts as a check valve, it has one end flanged according to UNE-EN 1092-2 PN10 and the other end with a strainer that prevents dirt from entering the line, in addition the passage is designed to be larger than the line itself, so we have minimal head loss. The valve strainer tends to become dirty over time, so it is important to check and clean the valve periodically for optimal performance.